Program
An ambitious research program
The climate crisis and the decline of biodiversity are forcing our societies to reinvent themselves. Nature-based Solutions (NbS) are approaches involving the protection, restoration, or management of ecosystems that effectively address a range of societal challenges, while generating positive impacts on the social, environmental, economic, and biodiversity fronts. Rooted in ecosystem functioning, NbS can complement, or even replace technological engineering solutions. They are attracting growing interest from a wide range of stakeholders, including local authorities and some private companies.
Co-led by CNRS and INRAE, the SOLU-BIOD National Research Program aims to promote scientific approaches that support the design, implementation, and evaluation of NbS. It also seeks to foster the emergence of a new economic sector with strong social and environmental benefits.
The SOLU-BIOD programme is funded as part of the France 2030 investment plan, with a budget of €44.2 million over a 9-year period (2023–2032). It is carried out in close collaboration with public research communities and a wide range of societal stakeholders.
The French government has assigned CNRS and INRAE the scientific leadership of this program, which is operated by the French National Research Agency (ANR).
The national research program is carried out in close collaboration with the national public research community and a wide range of societal stakeholders.
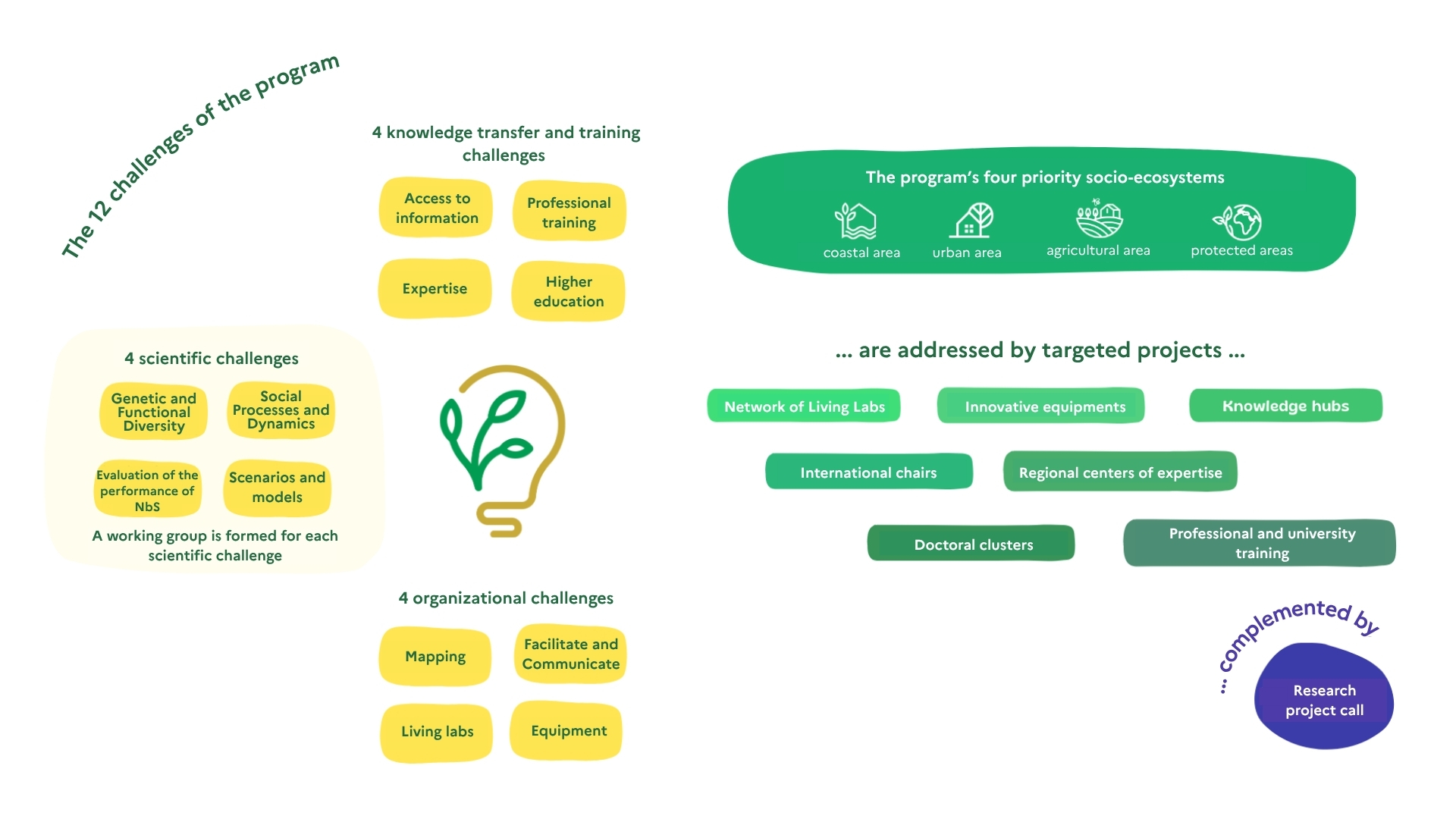
This program will tackle the barriers limiting the development of Nature-based Solutions (NbS) in France by addressing three challenges:
- Organizational challenge: How can we structure the French scientific community working on Nature-based Solutions (NbS)?
- Scientific challenge: How to guide the design, management, and evaluation of NbS in the context of global change?
- Knowledge transfer challenge: How to maximize access to knowledge and expertise, and adapt the topic of NbS to university and professional training?
The program will focus in particular on four key scientific issues:
- The role of social processes in the success of Nature-based Solutions (NbS)
- The evaluation of NbS performance and the mechanisms enabling their scaling up
- Scenarios and models to anticipate NbS performance in the context of global change
- The role of genetic diversity and evolutionary potential for NbS at different scales
Program framework
A brief overview of Nature-based Solutions
Nature-based Solutions (NbS) are approaches for the protection, restoration, or management of ecosystems that effectively address various societal challenges such as climate change, natural risk management, health, water supply, food security, and equity, while generating positive impacts socially, environmentally, economically, and for biodiversity.
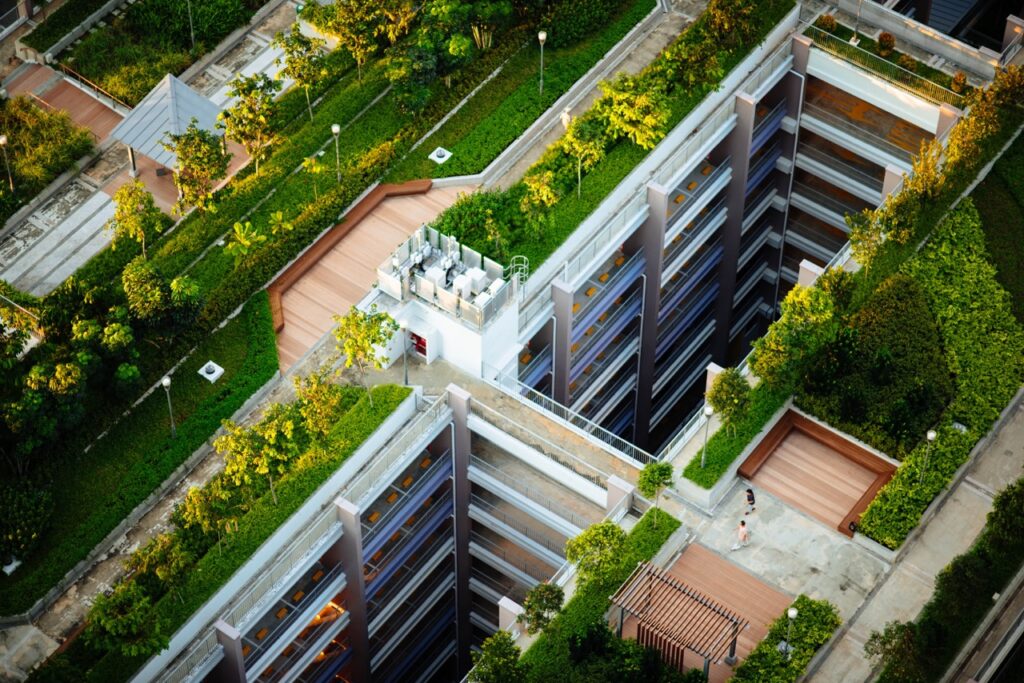

Urban greening (tree planting, creation of green spaces, green façades and roofs, community gardens) is an example of Nature-based Solutions (NbS). These approaches help reduce urban heat islands, improve soil permeability, combat pollution, and promote social inclusion.
Nature-based Solutions (NbS) can also be used to combat erosion in coastal areas. For example, planting suitable species along the coast, such as marram grass, a plant resistant to sand accumulation with a long and dense root system, helps stabilize dune sand, which acts as a barrier against wind and marine erosion.
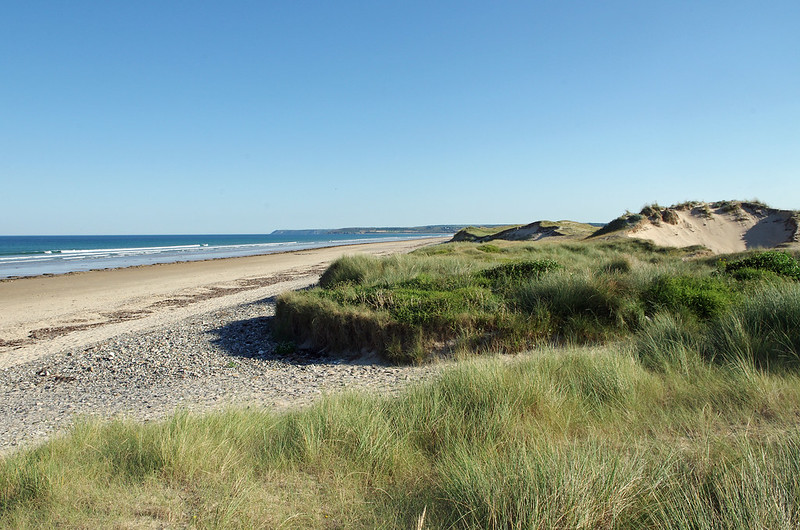

All these actions must benefit local biodiversity! Choosing suitable species and implementing actions at a sufficiently large scale are essential to establish viable Nature-based Solutions (NbS) in the long term.
Governance
To manage this program on behalf of the entire French scientific community and ensure the neutrality, quality, and transparency of the work, a multi-level governance structure has been established:
- A Program Management Team (CODIR), composed of the two Scientific Directors and the Program Manager, is responsible for coordinating and monitoring the program in relation to the Institutional Committee.
- A Pilots Committee, made up of members of the CODIR and representatives from the two lead institutions (INRAE and CNRS), is responsible for preparing meetings of the Institutional Committee and handling specific issues under the co-lead institutions’ responsibility.
- An Institutional Committee, composed of one representative from each partner institution of the program and chaired by INRAE and CNRS, is in charge of strategic guidance and validating the program’s orientations.
- Four Thematic Expert Groups—one for each key scientific challenge defined for the program—comprise 12 to 15 members from the scientific community and civil society. They support the program by refining the priority research questions that will be the subject of open calls for projects and dedicated knowledge hubs. More broadly, these experts help bring the vision and expectations of the community to the SOLU-BIOD governance.
- An International Scientific Committee (CS), composed of international experts with recognized expertise in the field of Nature-based Solutions (NbS), advises the Program Direction on research themes and activities to develop.
- A Stakeholders Committee, composed of representatives from major ministries, national organizations, associations, and socio-economic actors, facilitates the co-construction over time of the program’s research priorities and maximizes the uptake of research results by societal actors.
Partnership ecosystem
Program leads


Partners
Research and higher education institutions





Associated partners
Societal Stakeholders